
what we do
APPLICATIONS
A wide range of application is found in
almost every sector of activities viz
1. WATER PIPE LINES
WATER MAINS, PLUMBING,
SEWAGE SYSTEMS.
INDUSTRIAL WATER LINES,
PLANT PIPING.
DOMESTIC WATER SUPPLY.
2. AGRICULTURE & IRRIGATION
DEEP TUBE-WELLS & CASING PIPES.
3. GAS PIPE LINES
GAS, LPGAND OTHER NON-TOXIC GASES.
4. construction INDUSTRIES
SCAFFOLDING & STRUCURAL
PURPOSES.
5. CHEMICAL INDUSTRIES
CONVEYING OF CHEMICALS
6. FIRE FIGHTING SYSTEM AIR-CONDITIONING
ASH HANDLING SYSTEM.
8. OTHER PURPOSES
SUPPLY OF EXHAUST PIPING.
STEEL TUBES FOR IDLERS & TROUGHED BELT
CONVEYERS.
COLD STORAGE, SUGAR INDUSTRY.
LPG CYLINDER SUPPORTING
RINGS.
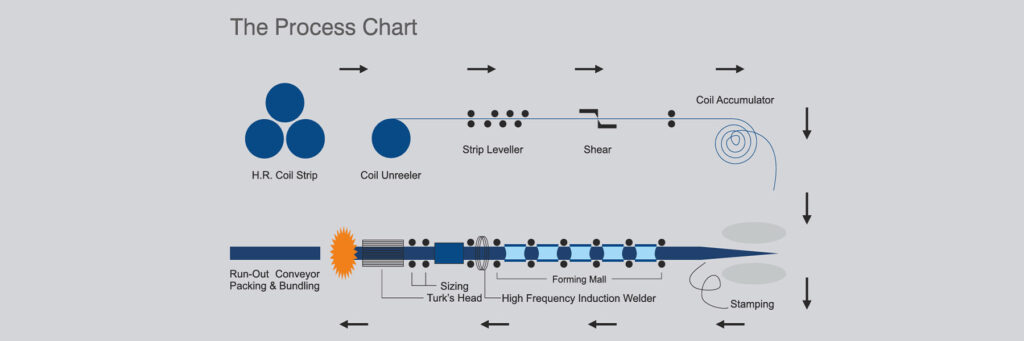
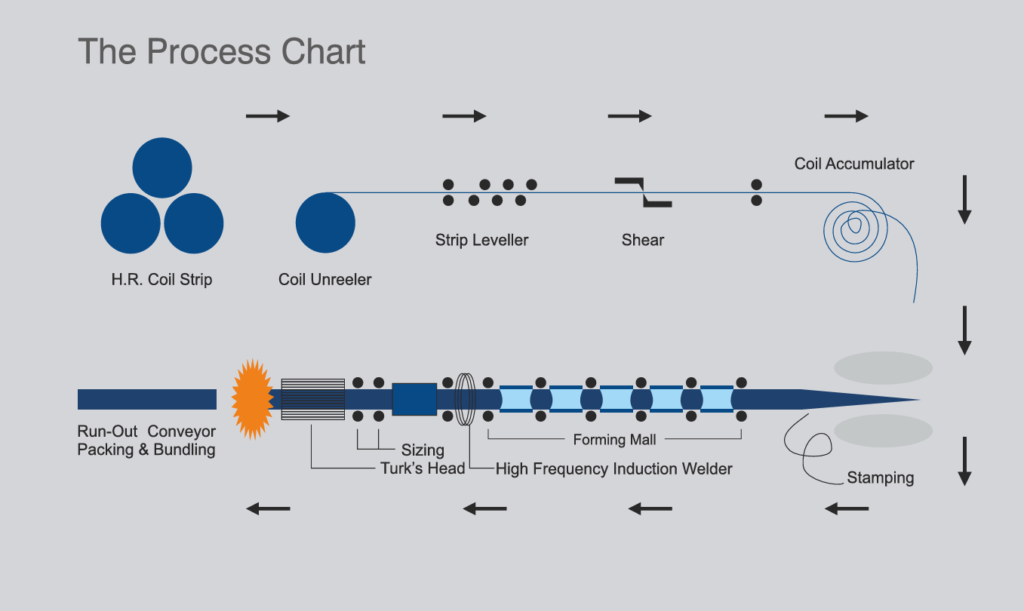
Manufacturing Process
ERW Pipes
ERW pipe is formed from hot-rolled coil produced in steel mill. All the incoming coils are verified based on the test certificate received from steel mill for their chemistry and mechanical properties.
The forming stage of ERW pipe begins with a single- width strip. The width of strip is roughly equal to the perimeter of the pipe to be produced. The edges of coil are sheared to pre-specified widths in slitting line.
The process involves uncoiling & leveling of coils and processing the same. The lead end of each coil is squared by shearing operation into the mill. Then this end is joined with coil end of outgoing coil to maintain continuity in production and reduce losses.
To maintain continuity of production, it is accumulated in an accumulator/loop pit. It is then gradually and continuously formed into a circular shape by shaped rolls as per the required diameter in forming stands arranged in tandem. In the welding stand, edges of formed strip are pre heated by High Frequency Electrical Induction heating process to the desired temperature, which are mechanically pressed together horizontally to form continuous weld seam. This welding process does not need any filler metal. Instead, the welding pressure causes some of the metal to be squeezed from the joint, forming a bead of metal on inside and outside of the tube. This bead or welding flash is trimmed during the process. The weld seam is examined and adjusted as per the weld parameters, including temperature and outside diameters. As per customer’s specification by induction heating process, to get fine grain structure in weld area. It is then cooled in open air followed by water quenching. Subsequently pipe string passes through sizing stands to obtain perfect roundness and diameter. Then pipes are cut to the desired length as per customer’s requirement on cutting car.
The forming stage of ERW pipe begins with a single- width strip. The width of strip is roughly equal to the perimeter of the pipe to be produced. The edges of coil are sheared to pre-specified widths in slitting line.
The process involves uncoiling & leveling of coils and processing the same. The lead end of each coil is squared by shearing operation into the mill. Then this end is joined with coil end of outgoing coil to maintain continuity in production and reduce losses.
To maintain continuity of production, it is accumulated in an accumulator/loop pit. It is then gradually and continuously formed into a circular shape by shaped rolls as per the required diameter in forming stands arranged in tandem. In the welding stand, edges of formed strip are pre heated by High Frequency Electrical Induction heating process to the desired temperature, which are mechanically pressed together horizontally to form continuous weld seam. This welding process does not need any filler metal. Instead, the welding pressure causes some of the metal to be squeezed from the joint, forming a bead of metal on inside and outside of the tube. This bead or welding flash is trimmed during the process. The weld seam is examined and adjusted as per the weld parameters, including temperature and outside diameters. As per customer’s specification by induction heating process, to get fine grain structure in weld area. It is then cooled in open air followed by water quenching. Subsequently pipe string passes through sizing stands to obtain perfect roundness and diameter. Then pipes are cut to the desired length as per customer’s requirement on cutting car.
Quality
Control
During production, online visual inspection is also carried out for surface defects, diameter accuracy, quality and weld bead shape. Required sample rings as per specification are cut to carry out mechanical testing of weld and body e.g. flattening test, bend test etc. All pipes are then processed in finishing and testing area for pipe end preparation i.e. Facing/Beveling followed by hydrostatic pressure testing as per specification.
Individual pipe is then visually inspected for the parameters specified in the specification before offering to the customer’s inspection, if any. Data of all tests is re- verified and submitted to the customers.
Individual pipe is then visually inspected for the parameters specified in the specification before offering to the customer’s inspection, if any. Data of all tests is re- verified and submitted to the customers.
LANDT
Hollow Section
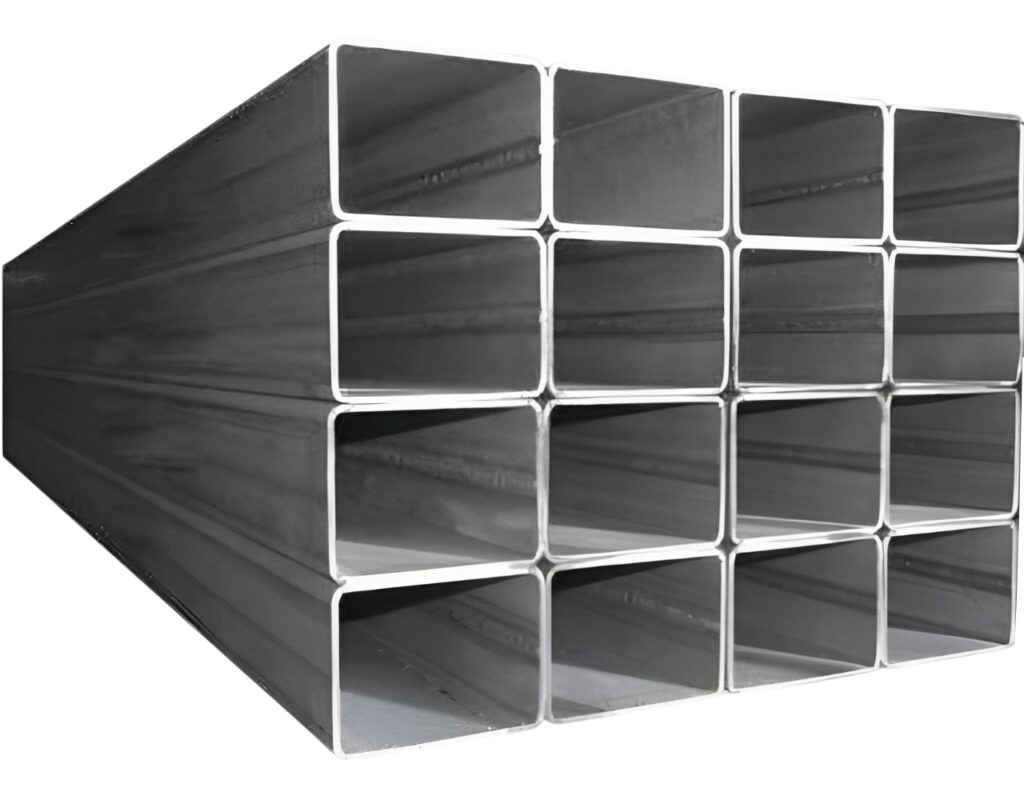

Steel hollow sections are the most versatile and efficient form for construction and mechanical applications. Many of the strongest and most impressive structures in the world today would not have been possible without hollow sections. The benefits of choosing Fortune Steel Hollow sections over other brands are-
• Manufactured from world class Hot Rolled Coils Smooth profile and less exposed surface acts as formidable barrier to rust
• Lesser painting and maintenance cost compared to traditional sections
• On earthquake resistant structures, the lower dead weight helps in reducing the design loads, thereby reducing the material cost of foundation
Lower handling cost, transportation cost, overall fabrication and erection cost.
• Manufactured from world class Hot Rolled Coils Smooth profile and less exposed surface acts as formidable barrier to rust
• Lesser painting and maintenance cost compared to traditional sections
• On earthquake resistant structures, the lower dead weight helps in reducing the design loads, thereby reducing the material cost of foundation
Lower handling cost, transportation cost, overall fabrication and erection cost.
